A U-value is a measurement that indicates a window’s glass or other material’s thermal efficiency – the lower a material’s U-value is, the longer it takes for heat to pass through.
As such, windows and doors with low U-values are ideal for houses and offices, as they’re excellent at keeping warm air in during the winter months, ensuring that the property is nice and cosy to live/work in and energy bills don’t get too high; something that is becoming increasingly important for homes across the UK.
As one would expect, older single-glazed windows have high U-values, while modern FINEO glass and double-glazed sash windows have low U-values.
When calculating a window’s U-value, there are three key factors to consider:
Uf Value: The frame’s thermal performance
Ug Value: The glass panel’s thermal performance
PSIG: The glass edge’s thermal performance
These three aspects, along with a handful of other measurements such as the window’s opening mechanism and design, determine the overall U-value. Thankfully, you don’t have to do all the work yourself, as a handful of U-value calculators online will crunch the numbers for you.
Whereas the U-value measures how good a window is at preventing heat loss, and Energy Rating takes numerous factors into account – such as G-value and L-factor – to give a window an overall energy efficiency score. G-Value measures the amount of the sun’s heat that will pass through the window, while L-factor measures how draught-proof and air-tight the window is.
The better a window’s Energy Rating, the better it will be at keeping a property warm and insulated.
A window frame’s material is a significant factor in its energy efficiency. Before purchasing a window unit, customers should consider the difference in energy efficiency between the standard options: Timber, PVCu and Metal.

Timber is a popular choice when prioritizing energy efficiency, as wood is naturally a great insulator. PVCu and Metal frames used to be synonymous with poor energy efficiency, though thanks to modern technology, today’s PVCu and lightweight aluminium frames are far more energy-efficient than ever before.
Results can vary significantly, so it’s always worth speaking to an expert before deciding on a window frame.
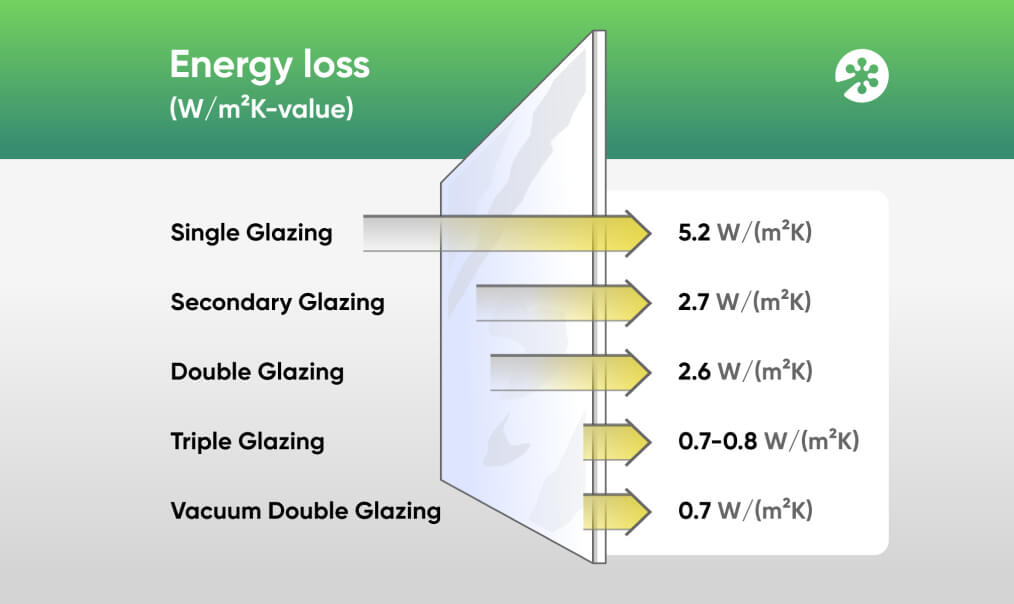
| Type window’s glazing | Average U-Value |
| Single Glazing | 5.2W/(m²K) |
| Double Glazing | 2.6 W/(m²K) |
| Secondary Glazing | 2.7W/(m²K) |
| Triple Glazing | 0.7-0.8 W/(m²K) |
| Vacuum Double Glazing | 0.7W/(m²K) |
With an average U-Value of just 0.7W/(m²K), our retrofitted sash windows with vacuum double glazing are at the top of the market for energy efficiency.
These efficient windows ensure that properties provide a cosy place to keep warm throughout the winter and prevent energy bills from getting too high.
New and replacement windows must have at least a ‘C’ Window Energy Rating and a U-Value that is no more than 1.6W/(m²K). This figure is often an eye-opener for those who still have singe-glazed windows, as they usually exceed the 5.0W/(m²K) mark, which would be illegal to install today.
It is legal to rent a property that still has single-glazed windows. However, the building’s landlord must ensure that the property has an overall Energy Rating of at least ‘E’. If a property doesn’t reach the ‘E’ mark, then replacing single glazed windows with vacuum double glazing is a popular and cost-effective way to improve an Energy Rating to its desired point.
A Passive House is a building that is extremely energy efficient and environmentally friendly. As the name suggests, a Passive House utilizes passive elements like sunshine and shading in place of central heating and air conditioning to keep the property warm and cool as required.
To be classed as a Passive House, a new building must meet a wide range of specifications referring to insulation, airtightness, heat recovery, and more. For a window to pass the strict Passive House guidelines, the entire window unit must have a U-value that doesn’t exceed 0.80W/(m²K).